What’s Link Building & Why Is It Significant?
 Whether you are new to link building or have been doing this for a while, we are confident that you’ll find something helpful in this guide. The nature of SEO and link building is always shifting, and now, the importance of building high-quality links has never been higher. The need to comprehend and implement high-quality SEO campaigns is essential if you’re going to compete and flourish on the internet, and that isn’t going to change any time soon. This manual is intended to get you moving quickly and in the ideal direction. There’s a whole lot to take in, but we’ve broken up everything into easy-to-digest chapters and also have included lots of examples along the way.
Whether you are new to link building or have been doing this for a while, we are confident that you’ll find something helpful in this guide. The nature of SEO and link building is always shifting, and now, the importance of building high-quality links has never been higher. The need to comprehend and implement high-quality SEO campaigns is essential if you’re going to compete and flourish on the internet, and that isn’t going to change any time soon. This manual is intended to get you moving quickly and in the ideal direction. There’s a whole lot to take in, but we’ve broken up everything into easy-to-digest chapters and also have included lots of examples along the way.
Link building is the practice of obtaining hyperlinks from other sites to yours. A hyperlink (normally just called a link) is a method for users to navigate between pages on the internet. Search engines use hyperlinks to crawl the internet; they search the links between the pages on your website and will crawl links between different sites. There are lots of techniques for building links, and while they vary in difficulty, SEOs often confirm that link building is one of the toughest elements of the jobs. Many SEOs invest the majority of their time trying to perform it well. Because of this, if you can master the craft of building high-quality links, it may truly put you ahead of the other SEOs and your competition.
Why Is Link Building Important For SEO?
The body of a hyperlink
To understand the value of link building, it’s important to understand the basics of how a link is created, how the search engines find links, and also what they can interpret from them.

Start of link label: Called an anchor tag (therefore the “a”), this opens the hyperlink tag and tells search engines a link to something else is going to follow.
Link referral location: The “href” means, “hyperlink referral,” and the text inside the quote marks indicates to which URL the link is pointing. This does not always have to be a web page; it could be the address of an image or a document to download. Sometimes, you will see something other than a URL, beginning with a # sign. These are neighborhood links, which require you to another section of the page you’re already on.
Visible/anchor text of connection: This is the little bit of text that users see the webpage, and on which they need to click on if they want to start the hyperlink. The text is usually formatted to make it stand out of the surrounding text, often with blue color and/or underlining, signifying to users that it’s a clickable link.
Closure of link label: This indicates the end of the hyperlink tag to the search engines.
What Hyperlinks Imply For Search Engines
There are two fundamental ways the search engines use links:
- To discover new web pages
- To help determine how well a page must rank in their outcomes
Once crawler bots have crawled pages online, they can extract the content of these pages and insert it to their indexes. In this manner, they can decide if they feel a webpage is of sufficient quality to be rated well for applicable keywords (Google created a brief video to describe that process). When deciding this, the search engines don’t just examine the content of the webpage; they also examine the amount of hyperlinks pointing to that page from external sites and the quality of those external websites. Broadly speaking, the more high-quality sites which link to you, the higher the likelihood you are to rank well in search results.
Links as a ranking factor are what enabled Google to start dominating the search market in the late 1990s. Founding member of Google, Larry Page, created PageRank, which Google used to assess the standard of a page partly based on the number of links pointing to it. This metric was subsequently used as part of the general ranking algorithm and turned into a strong signal since it was an excellent means of determining the standard of a webpage.
It was incredibly effective because it was based upon the idea that a connection could be regarded as a vote of confidence about a page, i.e., it would not acquire links if it didn’t deserve it. The theory being when someone links to a different website, they are effectively saying it’s a fantastic resource. Otherwise, they wouldn’t link it, much in precisely the way that you wouldn’t send a friend to a terrible place to eat.

However, blackhat SEOs soon discovered how to manipulate PageRank and search outcomes for selected keywords. Google began actively trying to find ways to discover websites that were manipulating search results, and began rolling out regular updates which were directly aimed at filtering out sites which didn’t deserve to rank.
It has also led to Google beginning to dismiss a number of link building methods that were formerly deemed fine, as an instance, submitting your website to web directories and receiving a link in return. This was a method that Google really recommended at one point, but it was abused and overused by SEOs. Therefore, Google ceased passing as much value with that type of link.
More recently, Google has actively penalised websites who have tried such overuse of these techniques–often known as over-optimisation–in their link building. Google’s routine Penguin upgrades are just one such instance. Knowing which link building techniques to prevent and keep within Google’s guidelines is an important subject that we’ll discuss later in this manual.
We don’t understand the full algorithm that Google uses to determine its search results–that’s the organisation’s “secret sauce.” Despite this fact, the overall consensus among the SEO community (according to the 2015 Moz search ranking variables survey) is that hyperlinks still play a major part in that algorithm. They represent the largest two pieces of the pie chart below.
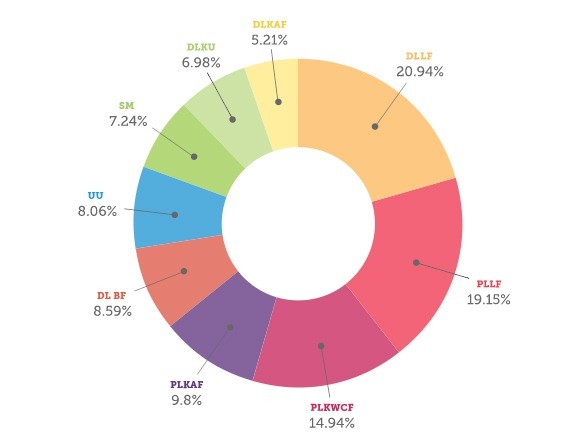
Domain-Level Link Features
(e.g., quantity of links to the domain name, trust/quality of hyperlinks into the domain, domain-level PageRank, etc.).
Page-Level Link Features
(e.g., PageRank, TrustRank, amount of link hyperlinks, anchor text distribution, quality of connection resources, etc…).
Page-Level KW & Content Characteristics
Page-Level, Keyword-Agnostic Characteristics
Domain-Level Brand Features
(e.g., offline use of brand/domain title, cites of brand/domain in news/media/press, entity association, etc…).
User, Usage, & Traffic Query Data
(e.g. traffic/usage signs from browsers/toolbars/clickstream, quantity/diversity/CTR of inquiries, etc…).
Social Metrics
Domain-Level Keyword Usage
(e.g., precise match keyword domain names, partial-keyword games, etc…).
Domain-Level, Keyword-Agnostic Characteristics
(e.g. domain length, extension, domain HTTP response time, etc…).
It is generally accepted that if the other factors are equal, the quantity and quality of links pointing into a page will make the difference between positions. Having said that, with recent movements in Google, for example, the launch of Penguin updates and its development of Google+, there is speculation that the impact of links is being reduced and substituted with social signals like tweets or +1s.
For now, however, there’s not much doubt that in the event that you get high-quality links to your website, you will rank better and gain more traffic (we’ll talk more about what makes a”good-quality” link later).
We’ve mentioned “high-quality” a several times, now, and it’s for a good reason: The focus on quality is rising as Google becomes more sophisticated at filtering low-quality hyperlinks. This directly affects SEOs, as they need to be certain the link construction techniques they choose focus primarily on that caliber.
There is an attribute that can at times be applied to links known as the “nofollow” attribute. If added, you won’t observe any difference if you are a user. However, if you look at the code of the link, It Is Going to look slightly different:

This tells Google to not pass any PageRank through this link to the target URL. Effectively, you are telling Google to not trust this link and to dismiss it from consideration. Therefore, it ought not to assist the target URL to rank any better.
The principal reason a site might use nofollow relates to scenarios where a website lacks complete control over the links added to its pages. In other words, they don’t wish to reveal to Google a vote of confidence when they do not know whether or not they actually are confident. That is much more common than you’d expect; here are a few examples:
- Blog comments
- Forum posts
- Guest book comments
- Yahoo! Replies
- Guest post signatures
Users can freely add links to each one of those places, and because of their size, it is not really practical to mediate every single one of these links. Thus, in order to discourage link spammers from taking advantage of a site’s PageRank, the website will often choose to blanket apply the nofollow attribute to all links posted.
Another use for the nofollow feature is for advertisers to utilise on links that were paid for. So, if you get an ad banner on a website which links back to your site, Google says the nofollow link should be added so that they understand to not pass any PageRank. The idea here is that you shouldn’t take advantage of the natural results by buying ads which have hyperlinks on other sites.
These are all examples where using nofollow is entirely appropriate.
With respect to your work, you ought to be aware that hyperlinks that have the nofollow feature applied will probably not help your natural search rankings as well as accompanying links. That is not to say they’re not rewarding. After all, typical users don’t notice whether or not a link is nofollowed or not, and might click through and visit your website anyway. After all, that’s the point of buying ads online. That having been said, for the purposes of link building, you need most of your links to be followed and therefore quantified by Google.
How Can Link Building Benefit My Business?
As we have discussed, links are a very important signal that the search engines use to determine positions. Thus, we know that increasing the number of high-quality links pointing towards your site can significantly increase your chances of ranking well.
There are other benefits to link building, however, that may not be immediately evident yet still worthy of thought. As part of your overall SEO strategy, here are some things that can be added.
Building Relationships
Link building can involve outreach to pertinent websites and blogs on your business. This outreach often is related to the promotion of something that you have just generated, like a piece of content or an infographic. A common goal of outreach is to obtain a connection, but there’s much more to it than this: Outreach can help you build long-term relationships with key influencers on your business, and these relationships can mean that your company becomes highly regarded and trusted. This is invaluable, even when we overlook link building for a moment because we’re creating genuine evangelists and advocates for our business.
Sending Referral Traffic
We have talked about the effects of links on your positions, but what about the effects of links on traffic visitors? A fantastic link from a highly-visited website can lead to a growth in visitors, too. If it is a relevant site, odds are that the traffic is also relevant and may lead to an increase in earnings. Again, the value of a link isn’t just about SEO–it is about customers. Michael Elsberg wrote a guest post on Tim Ferri’s blog, which you can see is a great advert for this type of outreach. In addition, he composed a case study on Forbes, describing just how precious this guest article became to him.
“There is a big difference between being subjected to a massive audience,” he says,”and being vulnerable to a relatively smaller (but still big) audience that’s ridiculously enthused.”
To put it differently, the avid followers of one blog proved far more likely to take the recommendation of the blogger than viewers were to look closely at the anchor on CNN, even when the one group was bigger than the other.
Brand Construction
Some link building techniques, such as creating content, can show people the experience of your company, and this might go a long way toward building your brand. By way of instance, if you make a piece of content based upon industry data and publish it, you have a possibility of becoming well known for this on your own industry. Whenever you do outreach and try to have links to the content, you’re showing your expertise and asking different people in your business to help spread the word and show others the same.
An Important Notice On Link Building Versus Connection “Earning.”
Before creating links, you require something of significance to build links to. Frequently it’s the homepage of your website. More often than not, however, you build links to technical resources such as a blog post, tool, study, or picture. Sometimes these assets exist before you begin your link building effort. Other times, you create these tools, especially with the objective of constructing links in your mind.
This presents the concepts of connection earning and “deserving to rank.” All link building campaigns have to start with something worth linking to. It is very tricky to build links to low-value webpages, but when you begin with something genuinely precious that people find useful or share-worthy, link building is a simpler endeavor.